Creating a Project in XTM Cloud
In this Blog I will guide you through the process of creating a project in XTM Cloud, a powerful translation management system. You will learn how to set up essential details, configure workflows, and ensure a smooth translation process from start to finish. Let's get started!
After creating a user account, head over to:
Projects > Project List
Click the Add Project button (typically located in the top-right corner).
Project Creation Wizard will open.
Add Customer Name: Select from existing clients or add a new one.
Project Name: Enter a unique identifier for easy tracking.
Reference Materials (optional): Upload glossaries or guidelines to ensure consistency.
Define the Source Language (the original text’s language).
Select one or multiple Target Languages for translation.
Choose Translation Memory & Machine Translation options (if applicable).
Upload your file

The Project Editor interface allows project managers to configure essential details, track progress, and assign translators. In the Workflow section, tasks are assigned to specific linguists, ensuring a structured process for translation and review. Each task includes word count tracking, due dates, and assignment settings to optimize efficiency. The interface also offers options to save workflow templates, start tasks, and send notifications to team members. This setup ensures a seamless translation management experience.
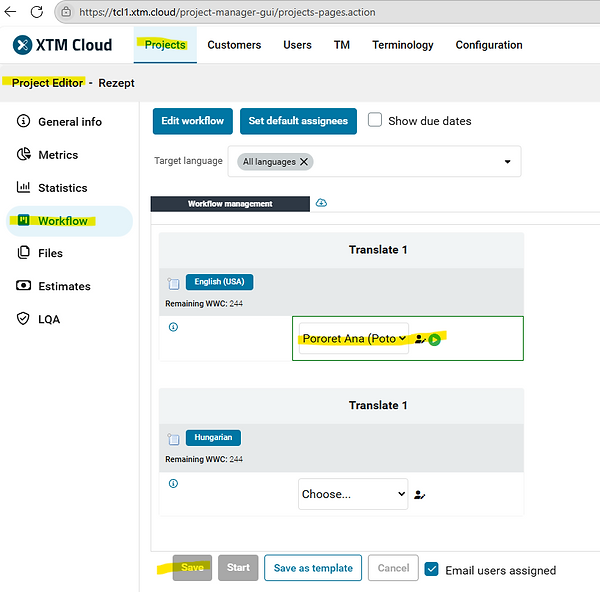
To verify the project, you navigate to the Workflow section and locate the file that needs translation. Next to the file name, there is a menu icon that allows you to open XTM Workbench, which provides a preview of the translator’s interface. This preview lets you see how the translation segments are displayed, ensuring that the source text, target language setup, and workflow assignments are correct.
Once inside XTM Workbench, you can select a workflow step and choose to open it as yourself (the project manager) or as another user. This allows you to check whether the translation environment is properly configured for the assigned linguists. You can also review translation memory matches, terminology suggestions, and formatting settings.

